Aquatic Feed
At present, the main aquatic feed mainly includes fish feed, shrimp feed and crab and turtle feed. We are committed to providing customers with high-performance processing equipment and advanced processing technology.
In the production of Aqua Feed, it is important to ensure the ideal formulation for a complete diet for food fish or ornamental fish. More importantly, gentle processing into a product that can be preserved is crucial. The focus is on the extrusion process.
As a cooking and shaping process, this has a lasting impact on the end product characteristics. The pretreatment and past treatment processing steps also contribute to overall performance.
Extrusion of Aqua Feed
The single most important goal during production of fish feed is the creation of a complete diet that enables optimal ingestion. At the same time, feed should maintain the animal’s health. This will maximize the conversion rateand the meat quality while minimizing the costs.
Blending, mixing and grinding
Raw materials account for over 80% of total production cost, formulated and continuously optimized on the basis of commercial and nutritional criteria. A fine grinding system can reduce the raw component blend to an average particle size of about 100 to 250 microns.The blend is then conveyed pneumatically to the control sifter.
Control sifting
A sifter, especially suitable for processing finely ground for fatty fish feed formulations is required to eliminate insoluble substances like bones, scales, sand, and fibers, which can clog die holes smaller than 1.5 mm. For this reason, we recommends a mesh aperture smaller than 70% of the die hole diameter.
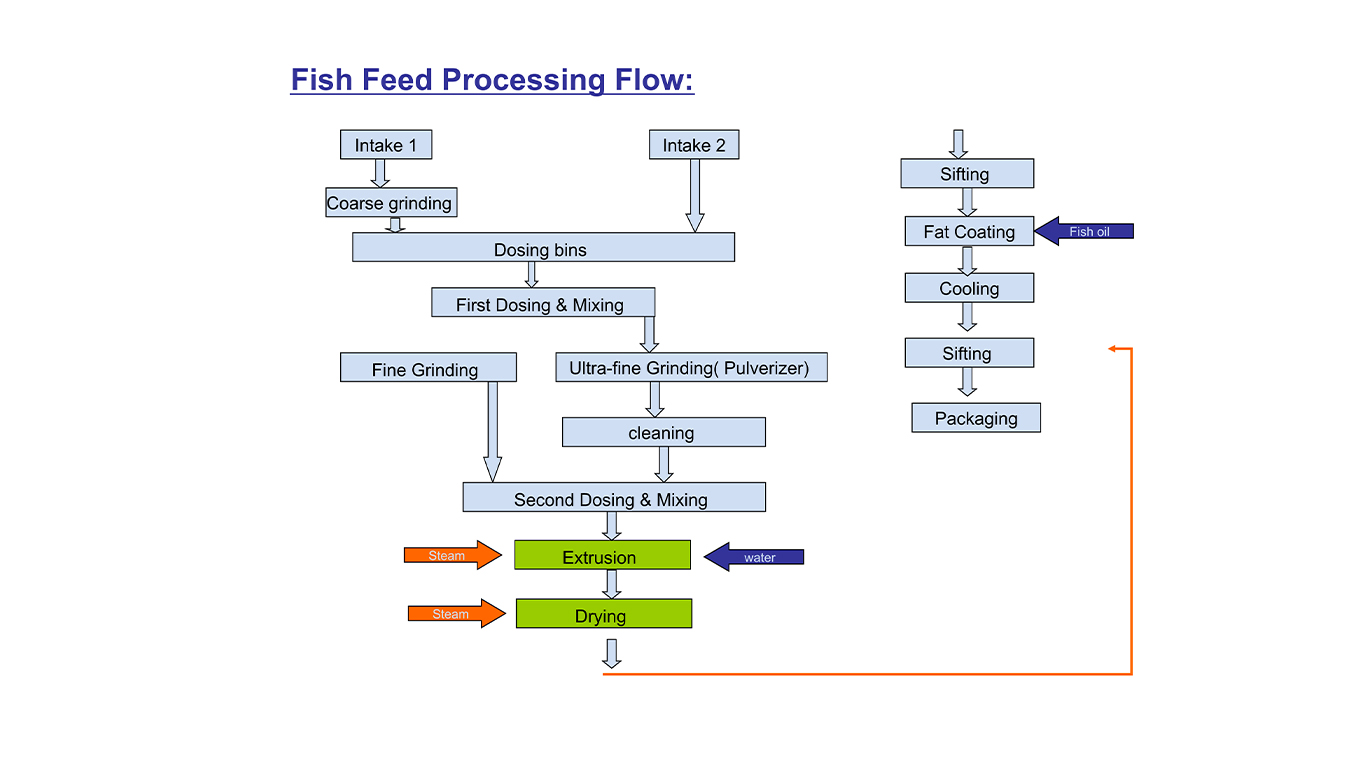
Extrusion process
The extrusion process is essentially a cooking process during which starch-containing components are decomposed and proteins are denatured. Combined with other ingredients, a hydrophil yet waterstable matrix is created.
The required heat is added mainly in the form of direct steam in the preconditioner. In the extruder, the mass, preheated to about 95 °C, is further heated by mechanical processing so that temperatures ranging from 120 to 140 °C are achieved. The patented “Density Control System” allows the steam pressure of the hot dough mass to be controlled while the mass is still inside the extruder. This enables the sinking or floating characteristics to be controlled across a wide range of bulk densities without compromising the cooking degree. The energy released from the extruder can be recovered almost without any emissions to the conditioning stage.
Shaping and Cutting
Die hole geometry is crucial in the process, as the hot product melt has to be depressurized, shaped, and cut, especially small die holes up to 0.8 mm require an optimized number of holes and a wear-resistant die plate. A movable cutting device enabled precise control with even knife exchange during the process. Since a considerable volume of moisture is evaporated at this point, the addition of hot air and a good aspiration is ecommended in order to prevent condensation and agglomeration of the products.
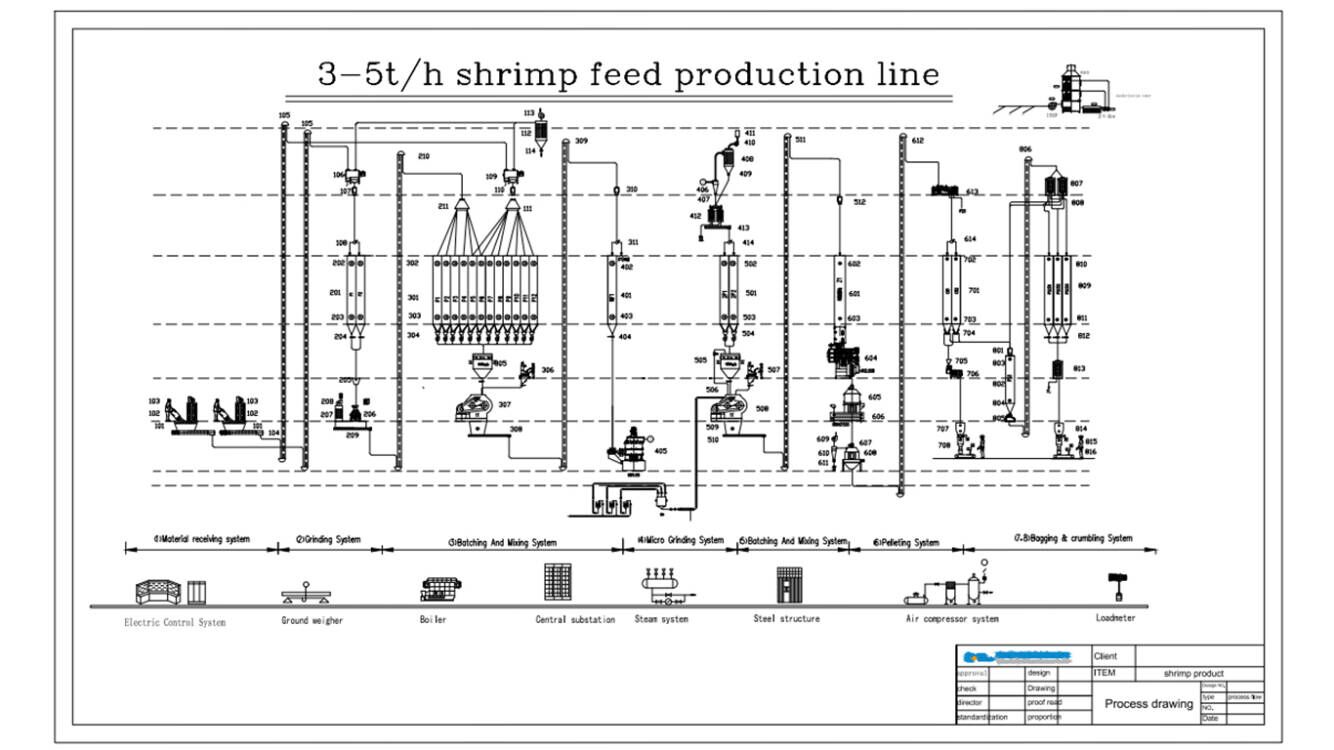
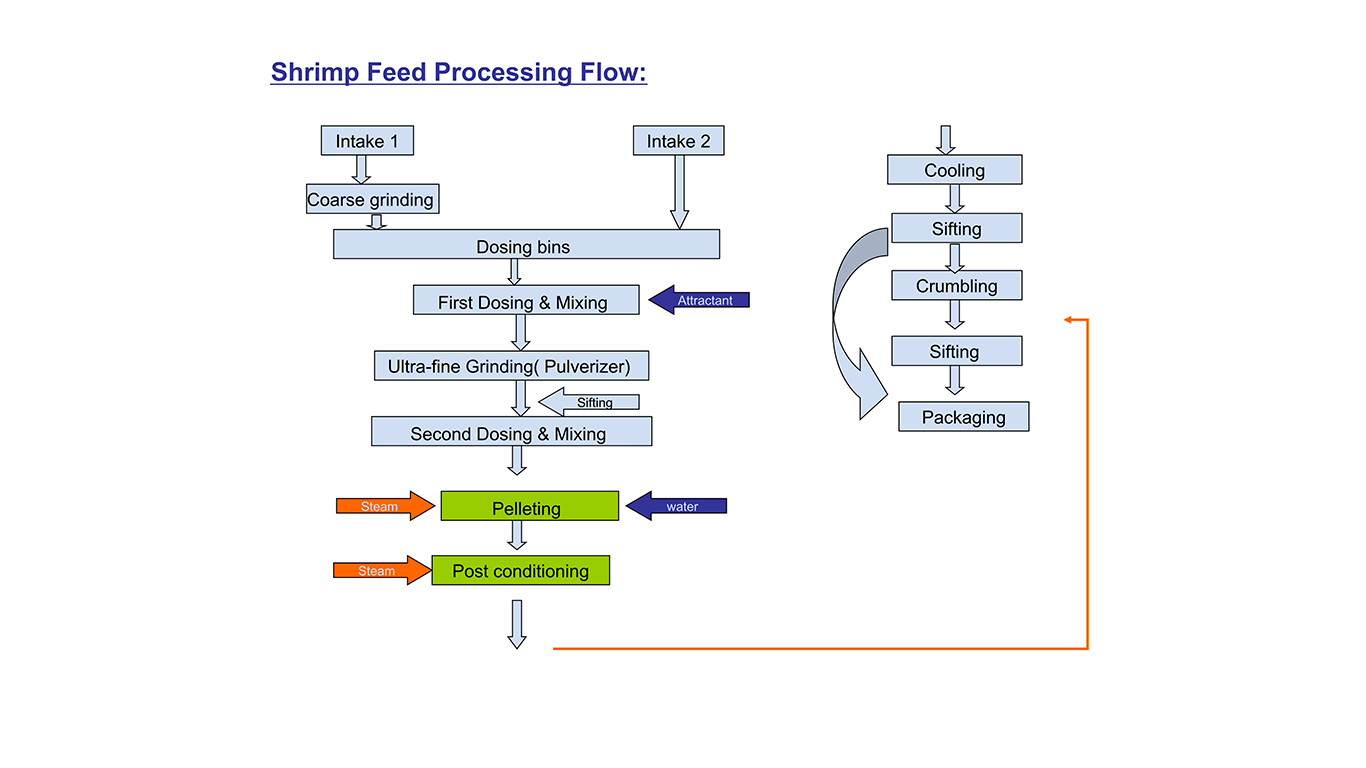
Introduction of shirimp feed processing technolegy:
Shrimp feed processing normally consist of raw materil receiving section, corase grinding system, first batching system, ultra-fine grinding system( pulverizer system) , second batching and mixing system,pelleting system, post-conditioning system, drying and cooling system, crumbler system, sifting system, packing system, the critical machine and process as following:
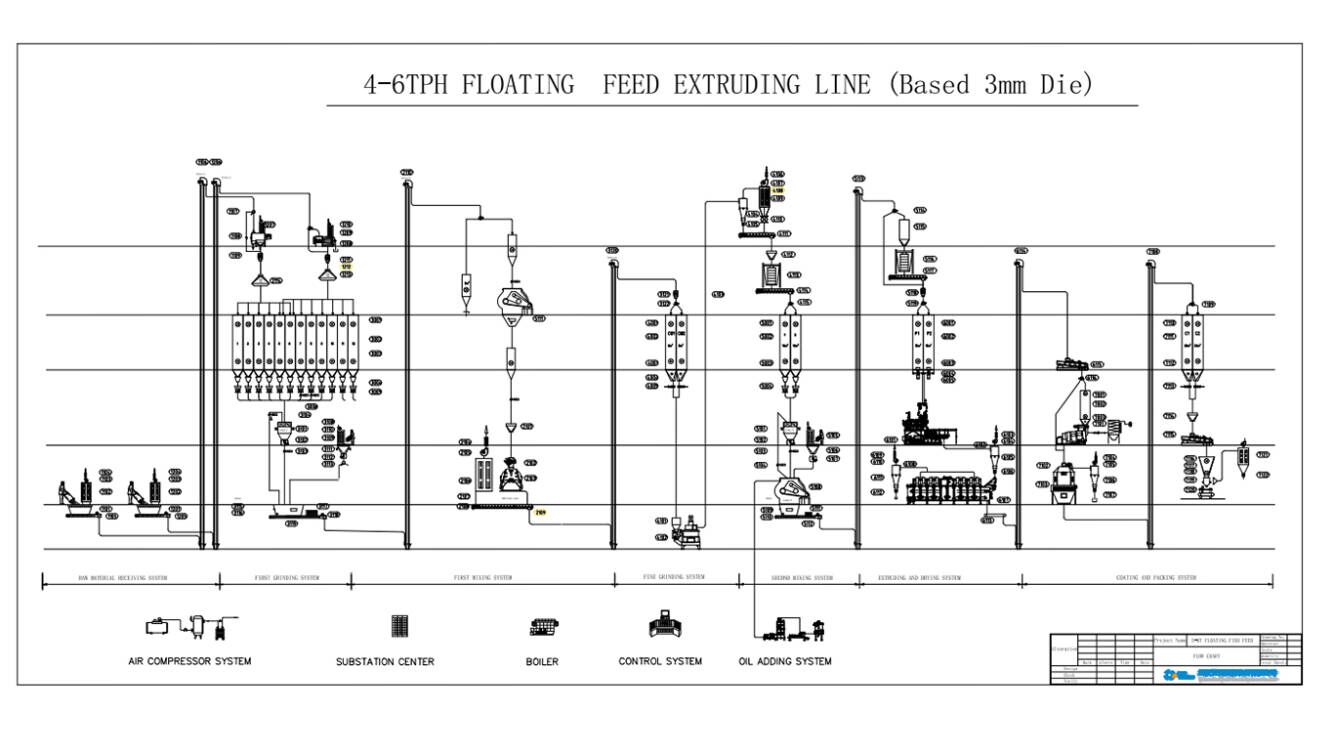
1) Pre –Grinding Systems (grinding takes place before blending )
Advantages:
• Allows blending of uniform particle size ingredients.
• Grinding system not linked particle size ingredients directly to production output Allows full capacity operation for long periods of time Multiple grinding systems can operate
simultaneously.
Pre-Grinding Equipment: Hammer mill :
• Low initial cost
• Grind most ingredients
• High capacity
• Low maintenance
2) Paddle Mixers:
• Complete mixing of partial batches.
• Good mixing of ingredients with dissimilar densities high percentage of liquids can be added.
3) Ultra-Fine grinding:
• Improved digestibility and nutrient absorption.
• Improve pellet strength and durability.
• Improve water quality in intensive and semi-intensive culture systems.
• Reduced wear and increased capacity of downstream equipment.
4) Weighing & Mixing
Addition of special feed additives.
• Coated vitamins.
• Carotinoids and other labile nutrients, stabilized in gelatin beadlets.
• Binders.
• Some types of phospholipid supplements.
5) Conditioning
Purpose:
• Mix (water, steam and oils with dry mash).
• Hydrate (diffuse moisture to the interior of feed particles).
• Heat (transfer heat energy from steam to feed particles).
Benefits:
• Increase life of pellet mill parts.
• Increase production rate.
• Improve product quality.
Importance of Water and Steam Control:
When water and/or steam does not enter the machinery at a constantrate it is very difficult to have consistent production.The correct water and steam pressuremust be delivered to theextruder, so the use of mechanisms to both regulate pressure and even the flow are important.
Pelleting:
Pellet mill consisit of screw feeder, conditioner , pellet press, most important parts is the ring die:
Pellet Dies:
Alloy dies are the choice for many feed processors because of their good abrasion and breakage resistance.Chrome dies have superior corrosion resistance, making them the choice for processing operations involving corrosive chemicals Carburized stainless dies have the best abrasion and breakage resistance as well as good corrosion resistance.
Post-Pellet Conditioning -------Starch Gelatinization & Binder Polymerization
Time> 15 minutes
Temperature> 85°C
Moisture = 14 to 17%
Drying:
Ideal Drying Parameters
• Average Moisture = 10 to 11%
• Maximum Pellet Temperature = 75°C
• Short Retention Time
Counterflow Coolers:
• Wide Particle Size Range
• Efficient Heat Recovery
• Low Maintenance
• Minimum space requirement .
Qualitative Water Stability Tests for Shrimp Feeds:
Water Absorption:
This test is a quick procedure for QC use during processing. It is based on the amount of water that is absorbed by pellets after 10 minutes.This has been generally correlated to water stability using visual assessments of pellet integrity after prolonged exposure to water.
Methods and Materials
Materials needed:
• 150g of sample.
• Paper cloth Water.
Equipment needed:
• Scale
• Thermometer
• Bucket
• Plastic sieve
Procedure:
• Weigh or tare a plastic sieve used to hold pellets.
• Weigh 100 grams of screened product.
• Place in the plastic sieve.
• Submerge in 25°C water for 10 min. DO NOT SHAKE.
• Remove sample from water and allow to drain for 5 min.
• Wipe off the plastic sieve with paper cloth.
• Weigh plastic sieve and wet sample and record final weight.
Results:
100< R < 140: Excellent.
141< R < 160: Good.
16 < R < 18 :Suspect.
R > 181: Bad.